How embedding models encode semantic meaning
Embedding models have long been a daunting concept for me. But what are they? And why are they so useful? Let's break it down in simple terms.
What's an embedding?
An embedding is basically a numerical representation of a piece of information - it could be text, audio, an image, or even a video. Think of it as a way to capture the essence or meaning of that information in a list of numbers.
For example, let's say we have this text: "show me a list of ground transportation at boston airport". An embedding model might turn that into something like this:
[0.03793335, -0.008010864, -0.002319336, -0.0110321045, -0.019882202, -0.023864746, 0.011428833, -0.030349731, -0.044830322, 0.028289795, -0.02810669, -0.0032749176, -0.04208374, -0.0077705383, -0.0033798218, -0.06335449, ... ]
At first, thus looks like a jumble of numbers. But each of these numbers points to a specific area within the embedding model's "space", where similar words or concepts might be located.
Visualizing embeddings
To help wrap our heads around this, let's look at a visualization. This beautiful image shows the entirety of the nomic-embed-text-v1.5 embedding model, as generated by this visualization tool:
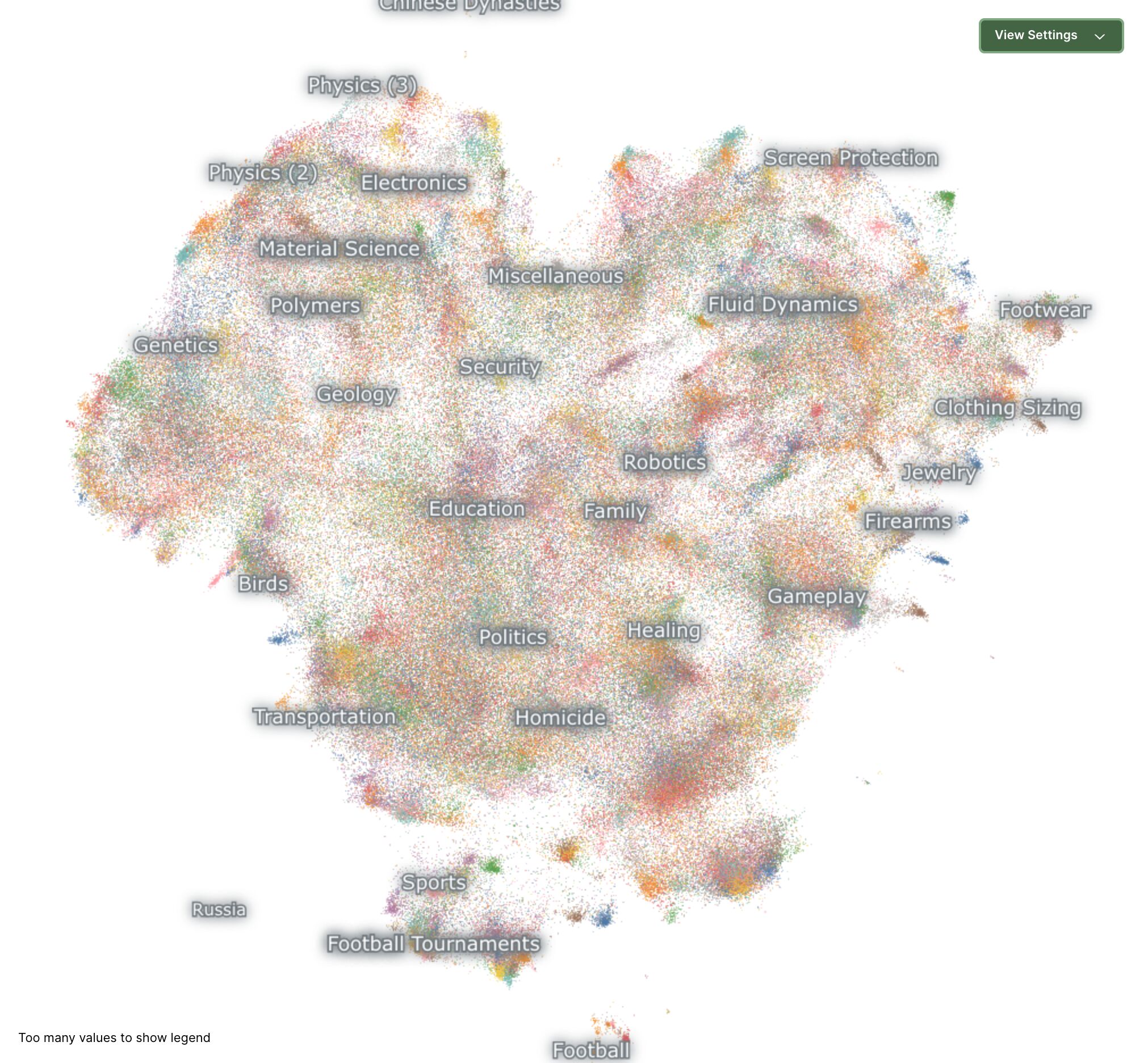
Now, if we take our example text about Boston airport transportation and plot its embeddings on this map, we'd see that some clusters are lit up, especially around "transportation". This means that the model has figured out that the topic of the query must be related to transportation in some way.
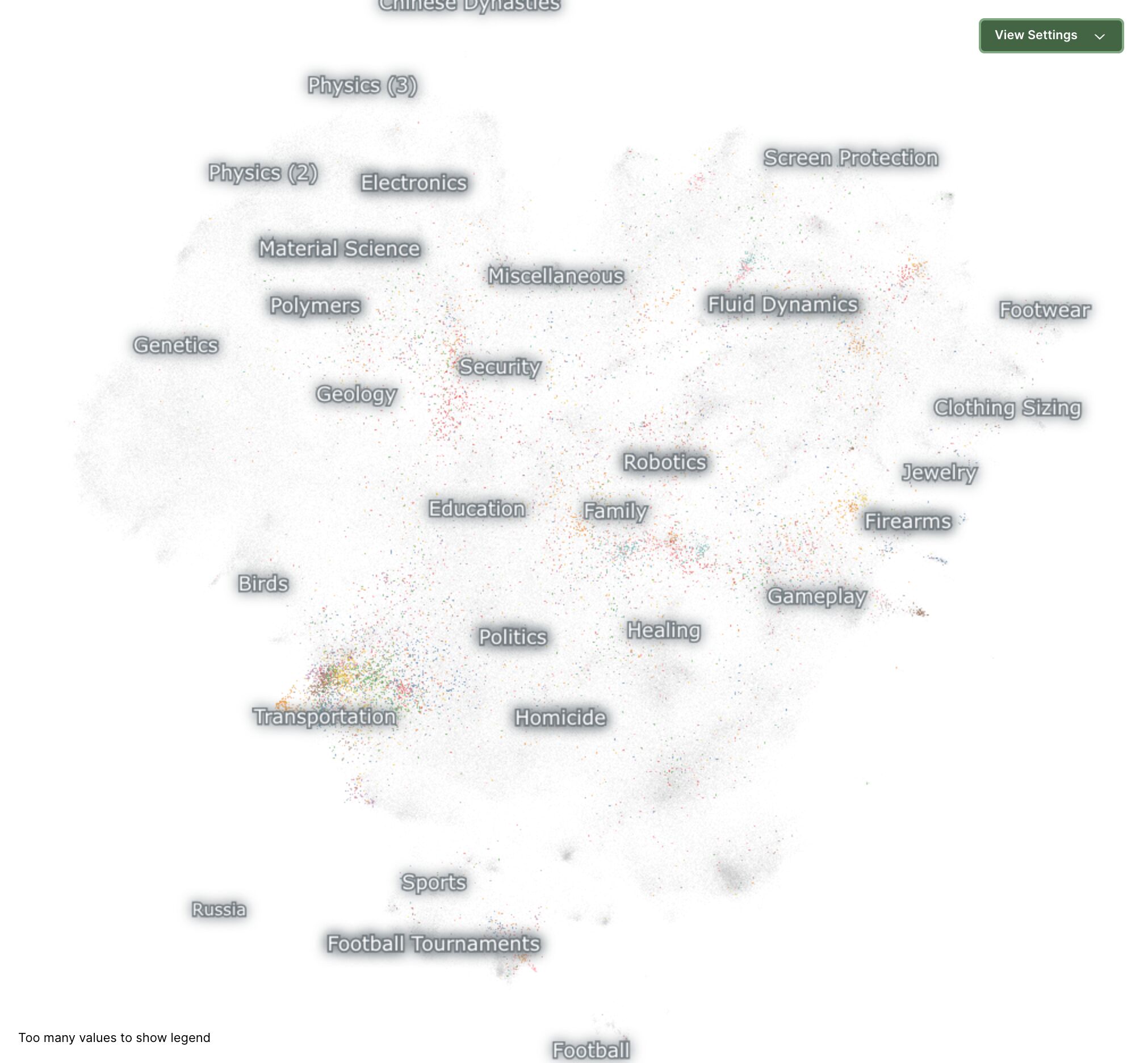
Zooming into this image, we can see more specific topics around transportation, like "Airport", "Travel" or "Highways" are lit up, which more closely matches our query.
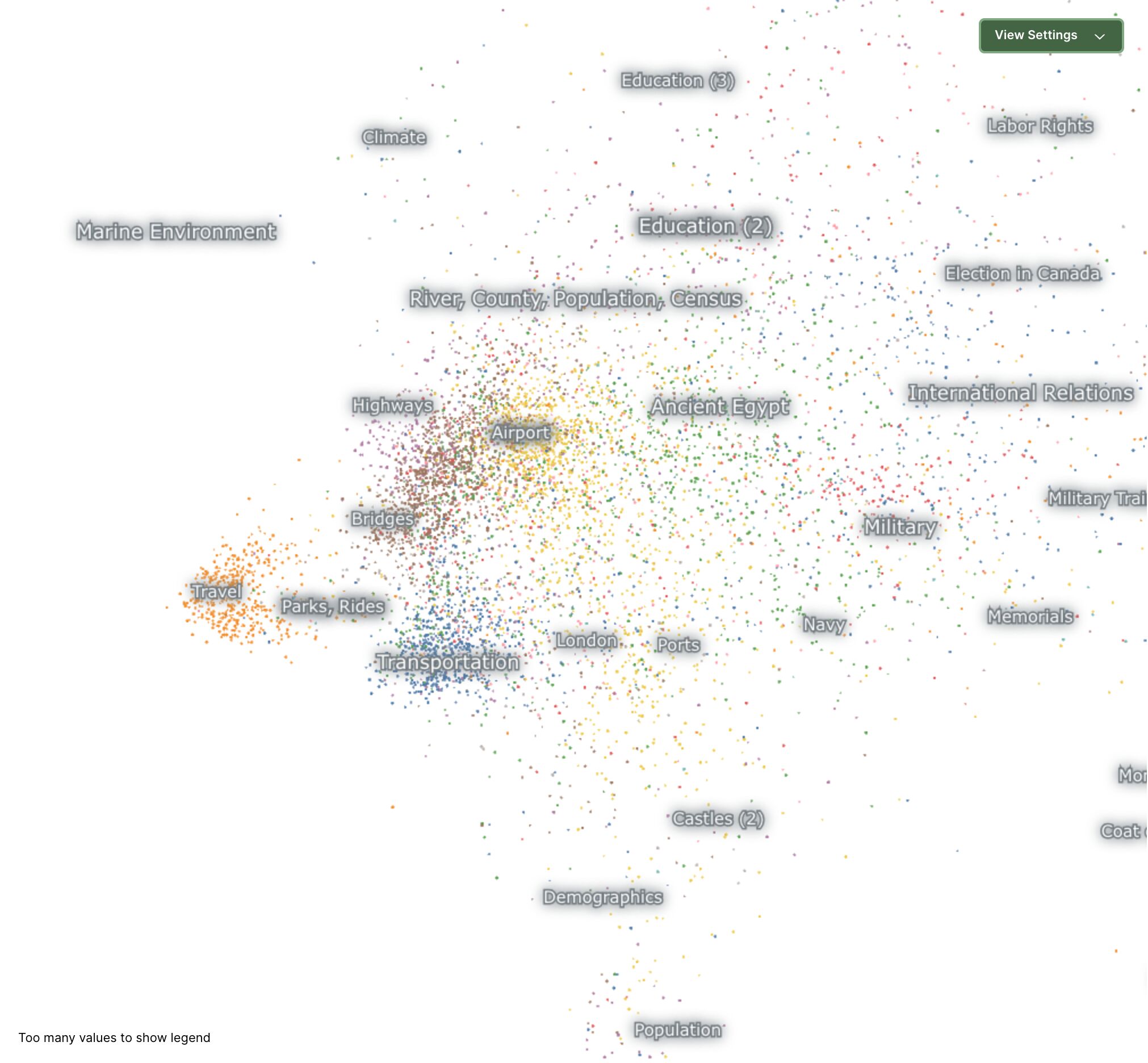
In a nutshell, embedding models are able to group terms by topics that are related to each other.
Why should we care about embeddings?
Encoding meaning in text has tons of different use cases. One that I'm particularly excited about is building RAG applications. RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation and refers to a method for Large Language Models (LLMs), where, given a question, you enrich the original question with relevant bits of information before answering it.
Here's how embeddings are useful for RAG:
- You have a bunch of documents in your data source.
- You use an embedding model to turn each document into a list of numbers (like we saw earlier).
- When someone asks a question, you also turn that question into a list of numbers.
- Then, you find the documents whose number lists are most similar to your question's number list.
- Voila! You've found the most relevant documents to answer the question.
This method is way better than previously used techniques like just searching for exact words in the documents. It's like the difference between having a librarian who only looks at book titles, and one who actually understands what the books are about.
Other things you can do with embeddings
Beyond RAG applications, embeddings are super useful for all sorts of things:
- Smarter searches: Find related stuff even if the exact words don't match.
- Better recommendations: "You liked this? You might also like these similar things!"
- Language translation: Help computers understand that "dog" in English and "perro" in Spanish mean the same thing.
- Sentiment analysis: Figure out if someone's happy or grumpy based on their tweet.
Wrapping it up
Embeddings are a clever way to turn words (or images, or sounds) into numbers that computers can understand and compare. By doing this, we can make emerging AI technologies a whole lot smarter at understanding language and finding connections between ideas.
Next time you're chatting with an AI or getting scarily accurate recommendations online, you can nod knowingly and think, "Ah yes, embeddings at work!"